17 Diseases You Can Catch From Your Dog

Dogs are often considered our best friends, showering us with affection and loyalty. Yet, behind those wagging tails and playful eyes, there are potential health risks that every dog owner should be aware of. While our pets enrich our lives in countless ways, they can also be carriers of diseases that can be transmitted to humans. Let’s explore the various diseases linked to dogs.
Rabies

Rabies is a disease known to target the nervous system. It is principally transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, such as a dog. Symptoms include fever, headache, and anxiety, followed by paralysis, delirium, and death if left untreated. Vaccination is essential for both dogs and humans to prevent this deadly disease.
Salmonellosis

While rare, dogs can carry Salmonella bacteria and spread it through their stool and saliva. This can lead to contamination of their environment. In humans, salmonellosis can cause symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal cramps, fever, and blood in the stool. If you suspect your dog might be a carrier, consult with a veterinarian.
Leptospirosis

This is caused by Leptospira bacteria, which thrive in warm, wet spots like damp grass and lakes. These bacteria can survive for over three months outside a host. Dogs often get infected through contact with contaminated urine, food, bedding, soil, or water. Humans can get it, too, so if your dog is diagnosed, seek medical advice.
Giardiasis

While the risk of catching Giardia from your dog is low, it’s still possible. This parasite spreads easily through water, food, surfaces, or objects. Always wash your hands after taking care of your dog’s poop to minimize the risk. In humans, Giardia can cause diarrhea, so maintaining good hygiene is key.
Cryptosporidiosis

Cryptosporidium, a tiny parasite, causes this issue, leading to diarrhea in animals and humans. The type most harmful to humans often comes from cattle. Dogs can transfer it from cattle to humans. Extra caution is needed for those with weakened immunity, such as individuals undergoing chemotherapy or living with AIDS.
Hookworm Infection
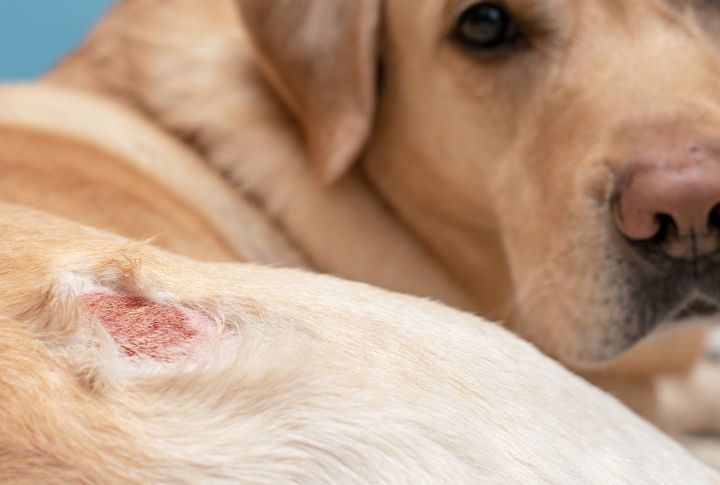

Hookworms can jump from dogs to humans indirectly. The eggs shed in your dog’s feces can contaminate the environment. When humans come into contact with these contaminated areas, they can develop cutaneous larva migrans (CLM), a condition that causes itchy, migrating skin rashes.
Roundworm Infection
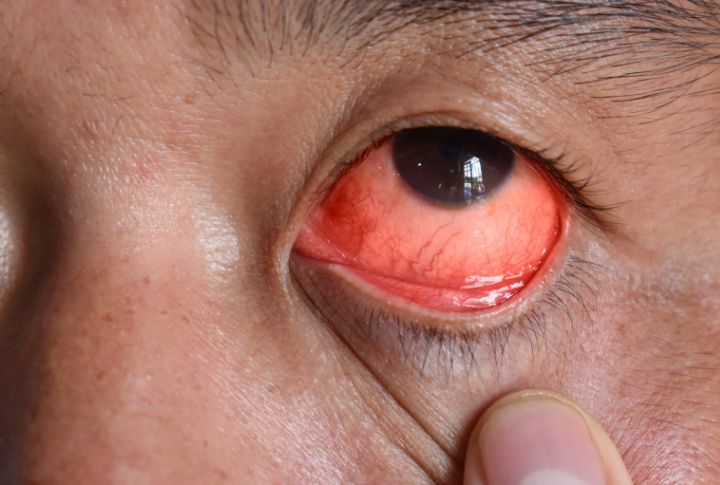
Coming into contact with dog feces can lead to roundworm infection in humans. These eggs can build up in areas where pets defecate, posing a significant health risk. Once infected, it can cause symptoms in the eyes, lungs, heart, and nervous system. Hence, always clean up after your pets and maintain proper hygiene.
Tapeworm Infection

Accidental ingestion of tapeworm eggs from dog feces can lead to tapeworm infection in humans. In this case, people become intermediate hosts, much like sheep, horses, or kangaroos. The eggs travel through the bloodstream, settle in organs, and form cysts filled with tapeworm heads.
Ringworm
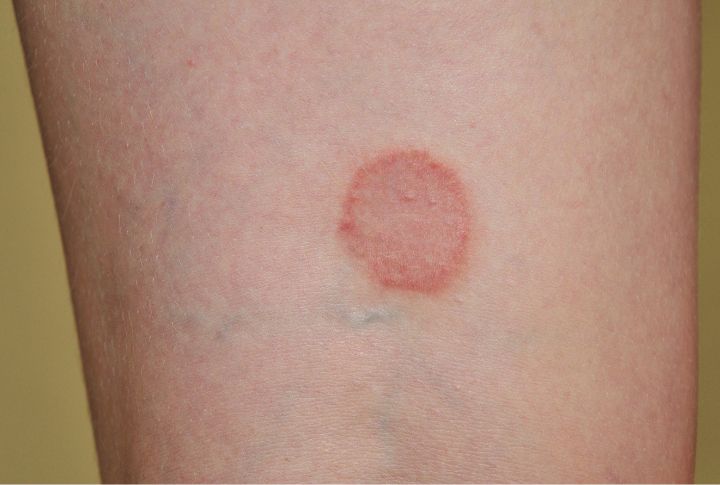
It can spread to people through direct contact with an infected dog. While healthy skin is generally resistant, those with scratches, wounds, or existing skin conditions like eczema are at higher risk. Children, senior citizens, and people with weaker immune systems are also more susceptible.
Mange

Sarcoptic mange, also called canine scabies, is a common type of mange in dogs that can be transmitted to humans. These mites cause itching and hair loss in people but cannot complete their life cycle or reproduce on human skin. Even minimal contact with an infected dog can result in transmission and discomfort.
Brucellosis

This can spread to humans through contact with an infected dog’s birthing fluids or vaginal discharge during whelping. Diagnosed with a blood test, the infection is treated with antibiotics for at least six weeks. Completing the full course is important, even if signs improve, as the infection can sometimes relapse.
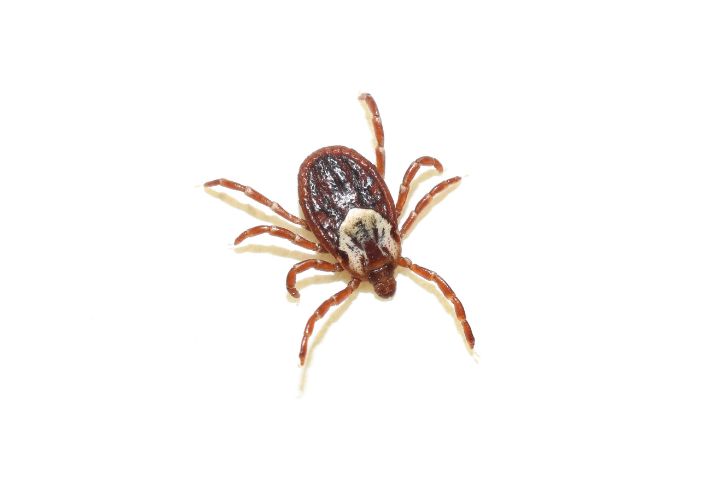
Lyme Disease

Ticks are the real troublemakers for Lyme disease, not a contagious spread. Dogs can pick it up from ticks in grassy or wooded areas. Although your dog won’t directly spread Lyme disease, they might bring ticks into your home. Regularly check both your pet and yourself to keep those ticks in check.
Ehrlichiosis

This disease is caused by bacteria from the Ehrlichia genus and is primarily transmitted by ticks. Humans can get ehrlichiosis from tick bites, and since dogs are more susceptible to ticks, people in the same household can test positive for ehrlichiosis. But don’t worry—with proper care, you can keep it at bay.
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever

Rocky Mountain spotted fever isn’t directly spread from dogs to humans but can be an indirect risk. If a dog is infected, ticks from that dog could bite people or other animals in the same environment. Infected individuals might experience fever, headache, rash, nausea, or stomach pain.
Bartonellosis
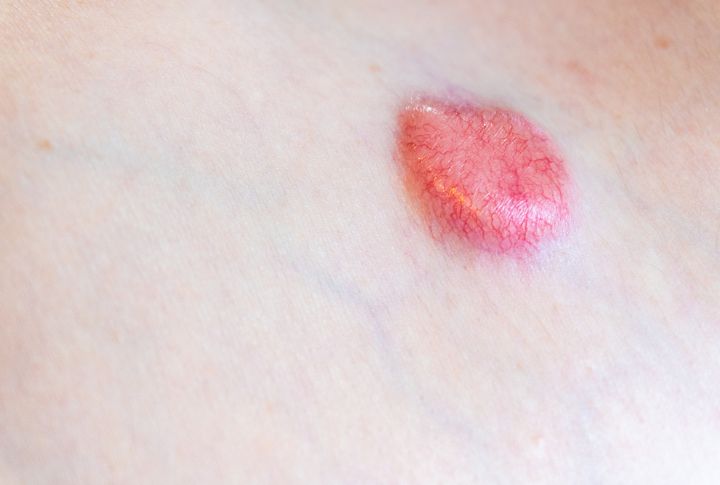
This infection shows up with a red bump where an insect bite or scratch occurs, and the symptoms look strikingly similar in both people and pets. If your furry friends have these red marks, it’s a sign they might have picked up Bartonella. To keep everyone safe, protect your pets from fleas and ticks.
Pasteurellosis
It follows a bite or scratch from pets, with Pasteurella multocida being the usual culprit. It can spread through inhaling droplets or by ingesting food and water tainted by the oral discharges of infected animals. Keeping bites and scratches clean and avoiding close contact with your pet’s face can help prevent this infection.
Leishmaniasis
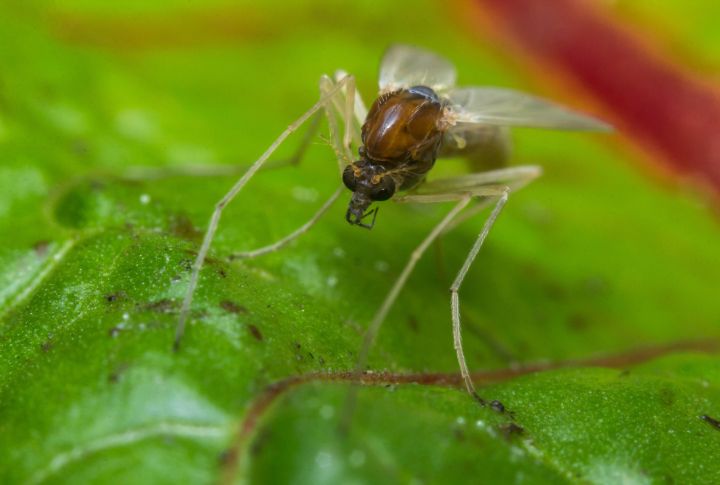

Sand flies are the main carriers of the Leishmania infantum parasite, which causes leishmaniasis. Dogs can harbor this parasite, turning them into reservoirs. Humans may become infected when sand flies bite your pet dogs. To reduce the chances of its spread, shield your pets from sand flies and be cautious in areas where these pests are prevalent.





